

Imagery


Imagery
![]()
心理訓練之目的,就是學習經常隨心所欲地製造一個完美的內心境界,協助運動員把技術發揮到淋漓盡致的地步(Williams 與 Straub,1993);影像訓練(imagery)就是心理訓練的其中一個重要手段。
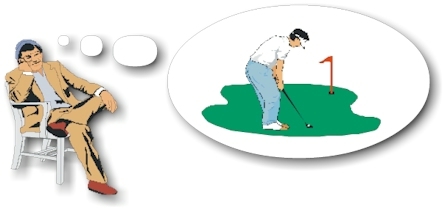
根據 Richardson(1967),影像訓練是指在沒有實際肌肉活動的情況下,在腦海中重演一些感受過的動作和形像。Richardson 還舉出了以下的一個例子:「當一個哥爾夫球手,閉上眼睛,坐在椅子上去想像擊球的動作時,就是正在進行影像訓練了」。通過影像訓練,運動員就能夠在記憶中再次經歷一些過往的景物或事件(Child,1986)。由於運動員在進行影像訓練的時候,通常都會想像自己的技術動作在完美無瑕的情況下完成,所以影像訓練還有增強運動員自信的好處(Singer,1986)。除了再次感受過往的經驗外,Vealey 與 Walter(1993)指出還可以利用影像訓練來創造新的體驗。
影像訓練的歷史背景,可追溯至 1892 年 Jastrow 研究當人進行思想活動時,實際上肌肉的活動情況為何(載於 Ross,1985)。自此以後,有關影像訓練的研究便相繼湧現,而主要的發現就是當人在想像某種動作或行為的時候,雖然並沒有實際的肌肉活動,但仍然會產生與實際活動相同的神經衝動,只不過在程度上是微弱得多罷了(載於 Murphy 與 Jowdy,1992)。
Orlick 與 Partington(1988)曾以 1984 年加拿大的奧運代表,合計 235 人作為研究對象,調查結果顯示,成績較佳的運動員,就算是平常練習的前一晚、練習當天的早上或前往練習的旅途中,他們都會用上影像訓練來為練習作好準備。他們通過影像訓練來完善技術、更正錯誤、想像自己演出成功和達到所定下的目標。在 Orlick 與 Partington 的研究之中,99% 的運動員聲稱有用上影像訓練,而且平均來說,他們每週會有 4 天,每天至少作一次為時約 12 分鐘的影像訓練,有部分運動員更報稱在奧運會比賽的地點,賽前會進行上 2 至 3 小時的影像訓練。此外,Gould,Tammen,Murphy 與 May(1989)的研究亦發現,80% 美國奧運代表隊的運動心理顧問有採用影像訓練來輔導運動員。

影像訓練的作用 |
|
影像訓練的透視形式 |
|
影像訓練的結果 |
|
進行一節影像訓練課 |
![]()
![]()
References
![]()
Child, D. (1986). Psychology and the Teacher (4th ed.). London: Cassell.
Gould, D., Tammen, V., Murphy, S., & May, J. (1989). An examination of U.S. Olympic sport psychology consultants and the services they provide. The Sport Psychologist, 3, 300-312.
Martens, R. (1987). Coaches Guide to Sports Psychology. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Murphy, S. M., & Jowdy, D. P. (1992). Imagery and mental practice. In T. S. Horn (Ed.), Advances in Sport Psychology (pp. 221-250). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Orlick, T., & Partington, J. (1988). Mental links to excellence. The Sport Psychologist, 2, 105-130.
Richardson, A. (1967). Mental practice: A review and discussion (Part I). The Research Quarterly, 38(1), 95-107.
Ross, S. L. (1985). The effectiveness of mental practice in improving the performance of college trombonists. Journal of Research in Music Education, 4, 221-230.
Singer, R. N. (1986). Peak Performance...and More. New York: Mouvement.
Vealey, R. S., & Walter, S. M. (1993). Imagery training for performance enhancement and personal development. In J. M. Williams (Ed.), Applied Sport Psychology: Personal Growth to Peak Performance (pp. 200-224). Mountain View, CA: Mayfield.
Williams, J. M., & Straub, W. F. (1993). Sport Psychology: Pass, Present, Future. In J. M. Williams (Ed.), Applied Sport Psychology: Personal Growth to Peak Performance (pp. 1-10). Mountain View, CA: Mayfield.
![]()

Back to Psychological Aspects of
Running
最近更新日期(Last Updated):2007-06-23